How to calculate employee stock options
By John Summa , CTA, PhD, Founder of HedgeMyOptions. The latter is the company that employs the grantee or employee. A grantee can be an executive, or a wage or salaried worker, and is also often referred to as the optionee. This party is given the ESO equity compensation, usually with certain restrictions. One of the most important restrictions is what is known as the vesting period. The vesting period is the time that an employee must wait in order to be able to exercise ESOs.
Exercise of ESOs, where the optionee notifies the company that he or she would like to buy the stock, allows the optionee to buy the referenced shares at the strike price indicated in the ESO options agreement.
What is the future value of my employee stock options? | Calculators by CalcXML
The acquired stock in whole or parts can then be immediately sold at the next best market price. The higher the market price from the exercise or strike price, the larger the "spread" and, therefore, the bigger the compensation not "gain" the employee earns.
As you will see later, this triggers a tax event whereby the ordinary compensation tax rate is applied to the spread. In other words, no matter how much higher the market price for the stock is, at the point of exercise you get to buy the stock at the strike price, and the bigger the spread between strike and market price, the bigger the earnings.
Vesting The ESOs are considered vested when the employee is allowed to exercise and purchase stock, but the stock may not be vested in some rare cases. It is important to read carefully what is known as the company's stock options plan and the options agreement to determine the rights and key restrictions available to employees. The former is put together by the board of directors and contains details of the rights of a grantee or optionee.
The options agreement, however, will provide the most important details, such as the vesting schedule, the shares represented by the grant and the exercise or strike price.
Of course, the terms associated with the vesting of the ESOs will be spelled out, too. For more on executive compensation limits, read How Restricted Stocks And RSUs Are Taxed.
Stock Plan Resource Center | cozosen.web.fc2.com
ESOs typically vest in portions across time in the form of a vesting schedule. This is spelled out in the options agreement. ESOs will normally vest at predetermined dates. Once all have vested, meanwhile, you can then exercise the entire group, or you can exercise part of the fully vested ESOs.

For more insight, read How do I "vest" something? You will need to come up with the cash to pay for the stock, but the price you pay is the strike price, not the market price withholding tax and other related state and federal income taxes are deducted at this time by the employer and the purchase price will typically include these taxes to the stock price purchase cost.
All details about vesting of ESOs should you be granted some or have some currently , can again be found in what is called the "options agreement" and "company stock plan".
Be sure to read these carefully, as fine print can sometimes hide important clues about what you may or may not be able to do with your ESOs, and exactly when you can begin to manage them effectively. There are some tricky issues here, especially regarding termination of employment either voluntarily or involuntarily. If your employment is terminated, unlike vested stock, you will not be able to hold on to your options before or after they are vested.
While some consideration may be given to circumstances surrounding why employment was terminated, most often your ESO agreement is terminated with employment, or just after. If options have vested prior to termination of employment, you may have a small window known as a grace period to exercise your ESOs. If you are hedging positions, the probability of employment termination occurring is an important consideration.
This is because if you lose the equity you are attempting to hedge, you are left holding hedges that are exposed to their own risk having no equity offset. If you have losses on your hedges and gains on your ESOs that cannot be realized, a large risk of loss is created.
Learn more about how hedging works in Hedging In Layman's Terms. The ESO Spread Let's take a closer look at the so-called "spread" between the strike and the stock price. As mentioned above, however, "gain" of intrinsic spread value is taxed as ordinary income , all due in the year you do the exercise. And what's worse, you receive no tax offset from the loss of time or extrinsic value on the share of the ESOs exercised, which could be considerable.
If you do not sell the stock, you are still subject to the tax upon exercise, an often overlooked risk. Any gains on the stock after exercise, however, would be taxed as capital gains , long or short term depending on how long you hold the acquired stock You would need to hold the acquired stock for one year and a day following exercise to qualify for the lower capital gains tax rate.
For more on capital gains taxes, see Tax Effects On Capital Gains. You would need to notify your company of the intent to exercise.
You would then be required you to pay the price of the exercise. But there is more. If these are non-qualified stock options, you would also have to pay withholding tax covered in more detail in the section of this tutorial on tax implications.
What is the future value of my employee stock options? | Calculators by CalcXML
This in-the-money amount is also your taxable income, an event looked at by the IRS as compensation increase, and thus taxed at ordinary income tax rates. Dictionary Term Of The Day.
A measure of what it costs an investment company to operate a mutual fund. Latest Videos PeerStreet Offers New Way to Bet on Housing New to Buying Bitcoin? This Mistake Could Cost You Guides Stock Basics Economics Basics Options Basics Exam Prep Series 7 Exam CFA Level 1 Series 65 Exam.
Sophisticated content for financial advisors around investment strategies, industry trends, and advisor education. Definitions and Key Concepts By John Summa Share. Introduction Employee Stock Options: Definitions and Key Concepts Employee Stock Options: Comparisons To Listed Options Employee Stock Options: Valuation and Pricing Issues Employee Stock Options: Risk and Reward Associated with Owning ESOs Employee Stock Options: Early Or Premature Exercise Employee Stock Options: Premature Exercise Risks Employee Stock Options: Of course, once you acquire the stock, if there are any price changes, assuming you do not liquidate , this will produce either more gains or some losses on the stock position.
The latter parts of this tutorial look at tax implications of holding the stock versus selling it immediately upon exercise. Holding part or all of the acquired stock raises some thorny issues regarding tax liability mismatching. This value, however, is not the only value on the options. An invisible value known as time value is also present, a value that is forfeited upon exercise.
Depending on the amount of time remaining until expiration the date the ESOs expire and several other variables, time value can be larger or smaller. Most ESOs have a stated expiration date of up to 10 years.
So how do we "see" this time value component of value? You need to use a theoretical pricing model, like Black-Scholes, which will compute for you the fair value of your ESOs. You should be aware that the exercise of an ESO, while it may capture intrinsic value, usually gives up time value assuming there is any left , resulting in a potentially large hidden opportunity cost, which may actually be larger than the gain represented by intrinsic value. For more on how this model works, see Accounting and Valuing Employee Stock Options.
The value composition of your ESOs will shift with movement of the stock price and time remaining until expiration and with changes in volatility levels. When the stock price is below the strike price, the option is considered to be out of the money also popularly known as "under water". When at or out of the money, the ESO has no intrinsic value, just time value the spread is zero when at the money. Since ESOs are not traded in a secondary market, you cannot "see" the value they truly have since there is no market price like with their listed options brethren.
Again, you need a pricing model to plug inputs into strike price, time remaining, stock price, risk-free interest rates and volatility. This will produce a theoretical, or fair-value, price, which will represent pure time value also known as extrinsic value. What to Expect in the Terms of the Grant With most ESOs, you can expect certain uniform conditions regarding basic terms.
For example, the exercise price is usually but not always designated as the market price of the stock on the day of the grant.
Also, the vesting period is probably going to be spread out across a number of years with a cumulative exercisable amount with each partial vesting date.
You would need one more year to vest the remaining shares. Finally, while typically a cash exercise is the only route allowed by some employers, others now allow cashless exercise. Here, an arrangement might be made with a broker or other financial institution to finance the exercise on a very short-term basis including withholding tax due on an exercise and then have the loan paid off with immediate sale of the all or part of the acquired stock.
With early exercise, you forfeit some profit back to your employer, and incur income tax to boot.
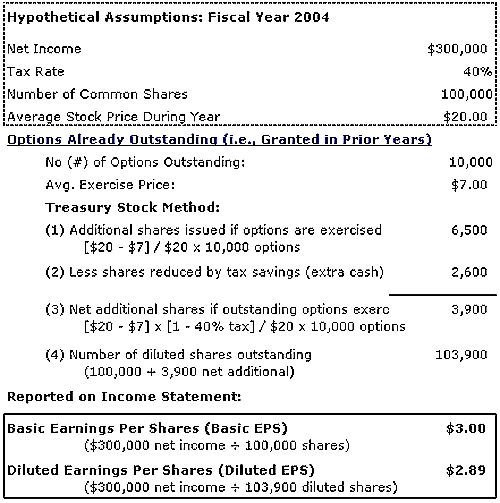
We look at strategies to help manage taxes and the exercise of incentive and non-qualified stock options. You may participate in both a b and a k plan.
However, certain restrictions may apply to the amount you can Generally speaking, the designation of beneficiary form dictates who receives the assets from the individual retirement Discover why consultant Ted Benna created k plans after noticing the Revenue Act of could be used to set up simple, Content Library Articles Terms Videos Guides Slideshows FAQs Calculators Chart Advisor Stock Analysis Stock Simulator FXtrader Exam Prep Quizzer Net Worth Calculator.
Work With Investopedia About Us Advertise With Us Write For Us Contact Us Careers. Get Free Newsletters Newsletters. All Rights Reserved Terms Of Use Privacy Policy.